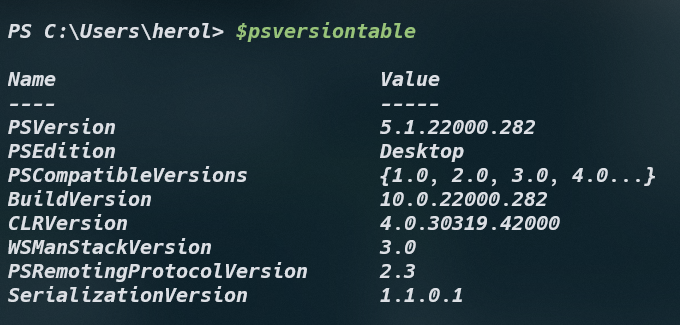
1. 查看powershell版本
2. 初识powershell
部分Linux 命令在powershell中都是可以使用的,所有powershell版本都向后兼容
PowerShell 命令称为 cmdlet;读作“command-lets”,当然,有些命令不属于cmdlet,比如函数等类型,在这一点上官网与书上显示的内容有些出入
powershell 命令一般都是使用动-名词格式 ,方便理解,但是显得十分冗长
2.1 Tab 键补全
powershell支持四种tab键补全,使用powershell ISE会有自动补全提示:
补全命令名:Get-S , 按下tab键后自动补全以get-s开头的命令
补全文件夹名:Dir C:\ , 按下tab键后遍历补全当前文件夹名
补全命令行参数:Get-ExecutionPolicy - ,不断按下tab键后,会在 - 后面显示可以使用的参数
补全参数合法值:Get-ExecutionPolicy -ErrorAction ,ErrorAction后面添加空格,然后不断按下tab键,会不断显示参数合法值
3. 使用帮助系统 3.1 更新帮助手册
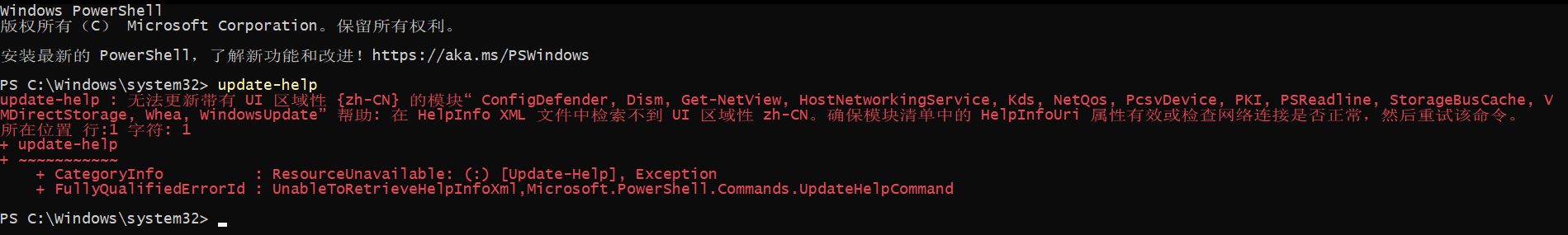
一开始使用帮助手册的时候打开会发现是空的,需要我们手动更新
以管理员的方式打开powershell控制面板
如果我们的系统语言设置成了中文,那么在更新帮助手册的时候会出错,这是应为帮助手册没有中文的,我们直接忽略掉即可。
虽然命令行下的帮助手册没有中文的,但是我们可以在微软官网上找到中文的帮助文档
3.2 使用帮助系统查找命令
Get-Help 可以查看命令的介绍,Get-Help 别名有 Help、ManGet-Help 可以搭配通配符使用, 案例如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 PS C:\Users\xxx\Desktop> Help Get-EventL *Get-EventLog Get-EventL * 帮助...oooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooo ]in an event log, or a list of the event logs, on the local computer or remote computers.Get-EventLog [-LogName ] <System.String> [[-InstanceId ] <System.Int64 []>] [-After <System.DateTime >] [-AsBaseObject ] [-Before <System.DateTime >] [-ComputerName <System.String []>] [-EntryType {Error | Information | FailureAudit | SuccessAudit | Warning }] [-Index <System.Int32 []>] [-Message <System.String >] [-Newest <System.Int32 >] [-Source <System.String []>] [-UserName <System.String []>] [<CommonParameters >]Get-EventLog [-AsString ] [-ComputerName <System.String []>] [-List ] [<CommonParameters >]-EventLog ` cmdlet gets events and event logs from local and remote computers. By default, `Get-EventLog ` gets logs from the local computer. Toparameter .-EventLog ` parameters and property values to search for events. The cmdlet gets events that match the specified property values.in Windows Vista and later Windows versions, use `Get-WinEvent `.NOTE ] > `Get-EventLog ` uses a Win32 API that is deprecated. The results may not be accurate. Use the > `Get-WinEvent ` cmdlet instead.
Help 命令并不是为了搜索Cmdlet命令,只是搜索关于命令的帮助文档,使用Get-command命令(别名Gcm)搜索Cmdlet命令使用Gcm命令如果不指定任何参数,则会输出所有类型的可能的命令,这个时候我们可以指定相应的类型,使用 -type参数来指定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 PS C:\> gcm -type cmdlet *log*----------- ---- ------- ------ Clear-EventLog 3.1 .0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.ManagementDisable-AppBackgroundTaskDiagnosticLog 1.0 .0.0 AppBackgroundTaskDisable-BcdElementEventLogging 1.0 .0 Microsoft.Windows.Bcd.CmdletsEnable-AppBackgroundTaskDiagnosticLog 1.0 .0.0 AppBackgroundTaskEnable-BcdElementEventLogging 1.0 .0 Microsoft.Windows.Bcd.CmdletsExport-BinaryMiLog 1.0 .0.0 CimCmdletsGet-DeliveryOptimizationLog 1.0 .3.0 DeliveryOptimizationGet-DeliveryOptimizationLogAnalysis 1.0 .3.0 DeliveryOptimizationGet-EventLog 3.1 .0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.ManagementImport-BinaryMiLog 1.0 .0.0 CimCmdletsLimit-EventLog 3.1 .0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.ManagementNew-EventLog 3.1 .0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.ManagementNew-FileCatalog 3.0 .0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.SecurityRemove-EventLog 3.1 .0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.ManagementShow-EventLog 3.1 .0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.ManagementTest-FileCatalog 3.0 .0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.SecurityWrite-EventLog 3.1 .0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.ManagementPS C:\>
3.3 参数 3.3.1 参数集
以下是Get-EventLog 语法的帮助部分, 以下笔记基于该部分
1 2 3 4 语法Get-EventLog [-LogName ] <System.String> [[-InstanceId ] <System.Int64 []>] [-After <System.DateTime >] [-AsBaseObject ] [-Before <System.DateTime >] [-ComputerName <System.String []>] [-EntryType {Error | Information | FailureAudit | SuccessAudit | Warning }] [-Index <System.Int32 []>] [-Message <System.String >] [-Newest <System.Int32 >] [-Source <System.String []>] [-UserName <System.String []>] [<CommonParameters >]Get-EventLog [-AsString ] [-ComputerName <System.String []>] [-List ] [<CommonParameters >]
该命令在语法中出现了两次,这表示该命令提供了两个不同的参数集,不同参数集中的参数不能够混用。有时候可以单独使用一个出现在两个参数集中的参数,这时候系统会默认使用第一个参数集中的参数。
方括号 [ ] 中的为参数名称,尖括号中的 < > 为参数值
3.3.2 可选和必选参数
当参数名和参数值同时 在方括号 [ ] 中时,表明该参数是可选的,如[<CommonParameters>],否则是必选的;如名称为LogName的参数,参数值<System.String> 未使用方括号 [ ] 括起来,表示这个参数是必选的。如果一开始没有指定必选参数而是直接输入命令,则会提示你输入相应的参数
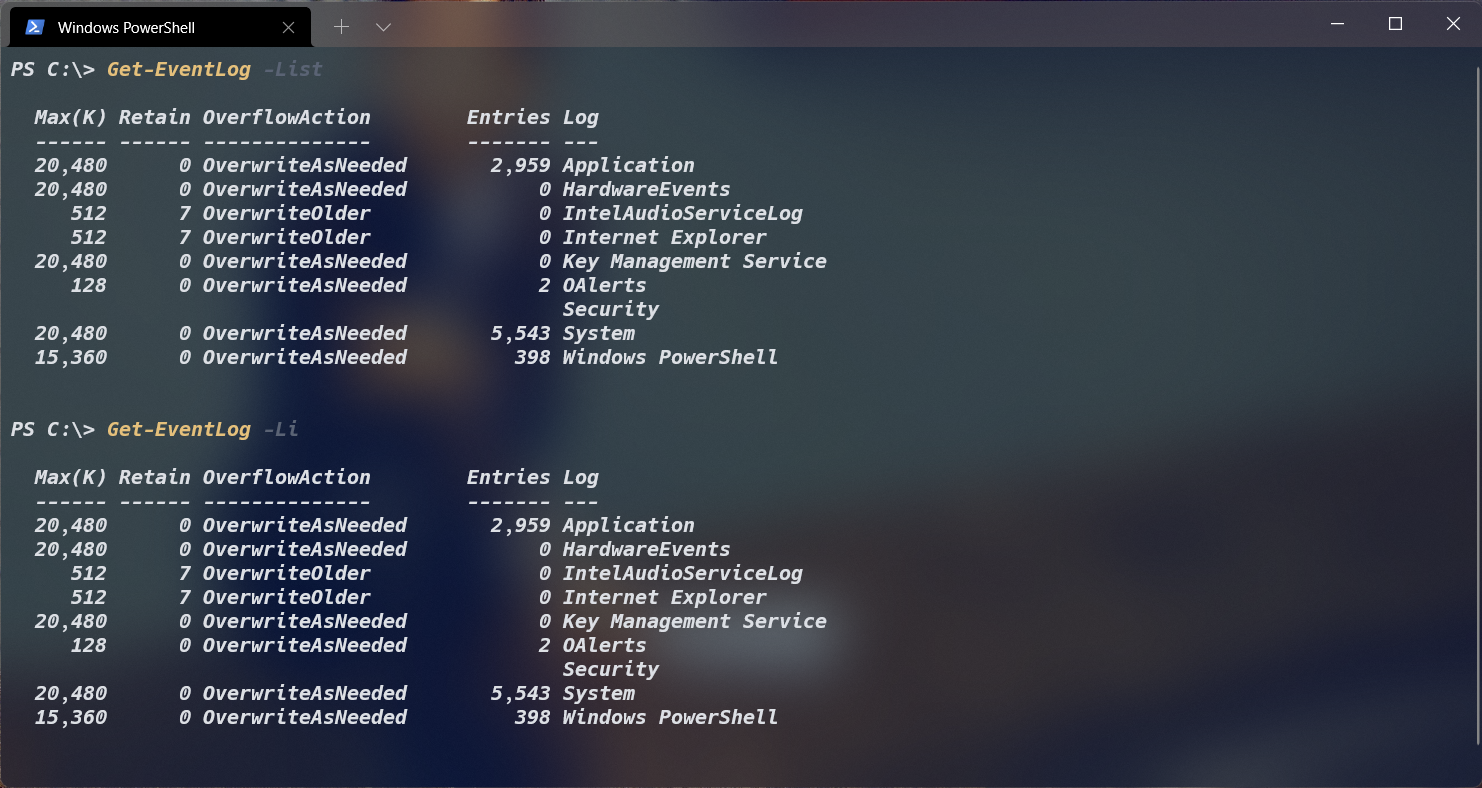
当选择一个参数时,不必要输入全部的参数名称,只需要输入可以让系统识别的不完整参数即可,但是不完整的参数一定要与其他参数区分,比如上面的例子中,-L参数不能表示 -List,还有可能表示 -LogName,若要表示 -List,可以表示为 -Li,如下所示:
3.3.3 位置参数
参数是具有位置性的,只要将参数值 放在正确的位置,则不需要输入具体的参数名称 。确定位置参数有两种方式,一种是通过语法概要 ,另一种是通过帮助文档 找到位置参数
1 Get-EventLog [-LogName ] <System.String> [[-InstanceId ] <System.Int64 []>] [-After <System.DateTime >]
a). 通过语法概要
只有参数名被方括号单独括起来 的的参数是位置参数,书中和微软powershell文档中并未说清楚,但是我在这个网站 找到了详细的解释
1). 第一个参数 -LogName,必选参数,因为参数名称和参数值不在同一个方括号 [ ]中,是位置参数,因为 -LogName在单独的方括号中
2). 第二个参数 -InstanceId , 可选参数,因为参数值在方括号中,是位置参数,因为-Instanceld在单独的方括号中
3). 第三个参数 -After,可选参数,因为参数值在方括号中,但是由于参数名称不在单独的方括号中,则若使用该参数时,必须使用该参数的名称或者至少是别名,不是位置参数,因为 -After不在单独的方括号中
综上所述,使用 Get-EventLog Application 0 是正确的,Application 和 0 分别赋值给了 -Logname和-Instanceld,但是使用命令 Get-EventLog 0 Application 是错误的,因为参数值的位置不对,不能被相对应的参数名称所接受。
b). 通过帮助文档
使用命令 Help 指定的命令 Full
案例:Help Get-EventLog Full,部分结果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 -List <System.Management.Automation.SwitchParameter>-LogName <System.String>-EventLog -List `. Wildcard characters are peparameter is required.0
如上所示,位置为数字则表示为位置参数,位置为named则表示不是位置参数
3.3.4 参数值
有些参数被称为开关参数,不需要输入任何参数值,在缩写语法中看起来是这样子的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 -AsString <System.Management.Automation.SwitchParameter>
通过<System.Management.Automation.SwitchParameter>表明这是一个开关参数
其他参数的数据类型一般被放在参数名称的后面,用空格与参数名称隔开,参数类型用尖括号< >括起来, 如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 -LogName <System.String>-EventLog -List `. Wildcard characters are peparameter is required.0
参数值中包含方括号表明可以接受数组、集合、或者是一个列表类型的字符串,如果字符串中有空格,需要将字符串参数用单引号' '括起来, 多个值使用逗号隔开
1 [-Index <System.Int32 []>]
3.3.5 发现命令示例
1 Help Get-EventLog -example
3.4 访问在线文档
1 Help Get -EventLog -online
4. 运行命令 4.1 命令结构
4.2 使用别名
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 PS C:\Users\herol> Get-Alias -Definition Get-Alias ----------- ---- ------- ------ gal -> Get-Alias PS C:\Users\herol> gal -def Get-Alias ----------- ---- ------- ------ gal -> Get-Alias PS C:\Users\herol>
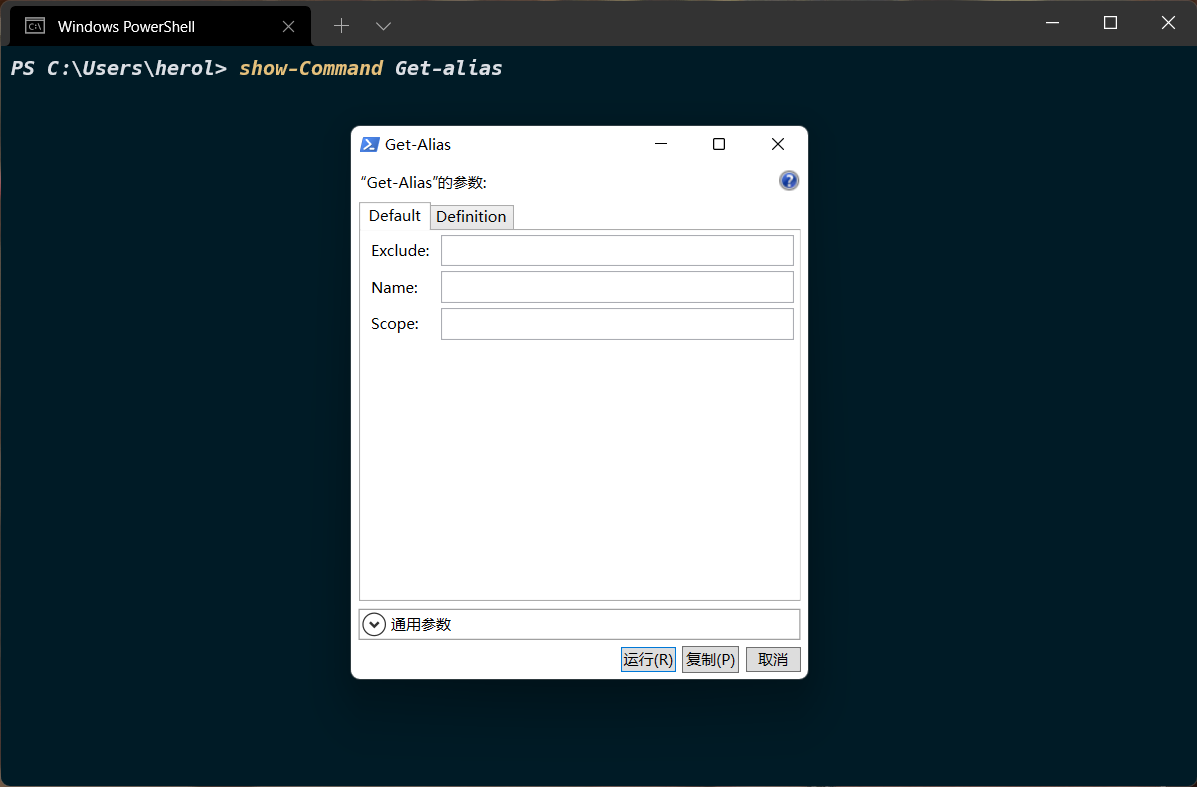
4.3 show-command
show-command 可以很清晰的让我们知道命令有哪些选项,当完成后可以单击运行,也可以点击复制将完成后的命令复制到剪切板。 show-command 必须是可以运行GUI的机器上才能够执行
4.4 对拓展命令的支持
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 PS C:\Users\herol> C:\windows\system32\sc.exe -- % qc bitsSC ] QueryServiceConfig 成功TYPE : 20 WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS3 DEMAND_START1 NORMAL-k netsvcs -p 0 PS C:\Users\herol>
书上44页还给出了另一种使用外部命令的方法,比较麻烦所以不再多说
*参考资料
对于powershell的学习,我是参考《Windows powershell 实战指南第三版》,书中共有28章节,我将拆分为4x7进行学习,每次学习4章节,总共学习7次。
powershell 适用于windows,mac以及Linux,但是相对于bash shell而言,powershell显得相对复杂了一点,powershell最先源于windows系统,后来开源后才发布了mac以及Linux版本,但毕竟源于Windows,运行在其他系统上在我看来不尽人意。
[[powershell魔改]]