Linux shell(5)-呈现数据
1. 理解输入输出
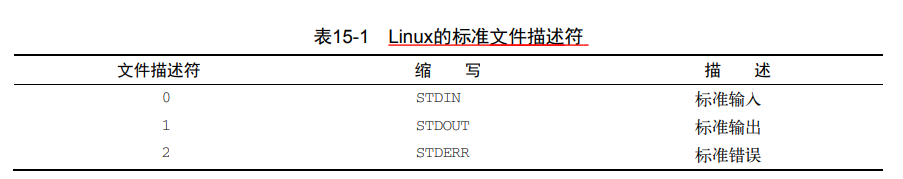
1.1 标准文件描述符
- 文件描述符表示对文件对象的描述,Linux有9个文件描述符,bash保留了前三个文件描述符(0、1和2)
0 代表标准输入,如键盘
1 代表标准输出,如显示屏
2 代表标准错误,一般也是显示屏
1.2 重定向错误
1.2.1 只重定向错误
- STDERR 文件描述符为2,该值必须紧紧地放在重定向符号前,否则不会工作。
1 | |
1.2.2 重定向错误与数据
- 如果想重定向错误和正常输出,必须用两个重定向符号。
1 | |
- 当使用&>符时,命令生成的所有输出都会发送到同一位置,包括数据和错误
- 为了避免错误信息散落在输出文件中,相较于标准输出,bash shell自动赋予了错误消息更高的优先级。这样你能够集中浏览错误信息了
2. 在脚本中重定向输出
临时重定向
永久重定向
2.1 临时重定向
- 在重定向到文件描述符时,你 必须在文件描述符数字之前加一个&:
1 | |
- 案例:
1 | |
2.2 永久重定向
如果脚本中有大量数据需要重定向,那重定向每个echo语句就会很烦琐。可以用exec命令告诉shell在脚本执行期间重定向某个特定文件描述符
案例:
1 | |
3. 在脚本中重定向输入
- exec命令允许你将STDIN重定向到Linux系统上的文件中:
1 | |
- 案例:
1 | |
- 将STDIN重定向到文件后, 当read命令试图从STDIN读入数据时,它会到文件去取数据,而不是键盘。
4. 创建自己的重定向
4.1 创建
在shell 中最多可以有9个打开的文件描述符。其他6个从3~8的文件描述符均可用作输入或输出重定向。
案例:
1 | |
- 在上面的案例中,演示了在脚本中临时重定向输出,然后恢复默认输出设置的常用方法。相当于我们C语言编程中学习的变量交换数值的那么一个过程
4.2 关闭
- 要关闭文件描述符,将它重定向到特殊符号&-。见案例1.
1 | |
- 在关闭文件描述符时还要注意另一件事。如果随后你在脚本中打开了同一个输出文件,shell 会用一个新文件来替换已有文件。这意味着如果你输出数据,它就会覆盖已有文件。见案例2。
- 案例1:
1 | |
- 案例2:
1 | |
5. 列出打开的文件描述符
因为它会向 非系统管理员用户提供Linux系统的信息,所以许多Linux系统隐藏了该命令
在很多Linux系统中(如Fedora),lsof命令位于/usr/sbin目录。要想以普通用户账户来运行 它,必须通过全路径名来引用:
$ /usr/sbin/lsof这里不多加描述,需要的自行百度
6. 阻止命令输出
- 可以将STDERR重定向到一个叫作null文件的特殊文件。null文件跟它的名 字很像,文件里什么都没有。shell输出到null文件的任何数据都不会保存,全部都被丢掉了。
- 在Linux系统上null文件的标准位置是
/dev/null。你重定向到该位置的任何数据都会被丢掉, 不会显示 - 由于/dev/null文件不含有任何内容,程序员 通常用它来快速清除现有文件中的数据,而不用先删除文件再重新创建。
1 | |
7. 创建临时文件
- 系统上的任何用户账户都有权限在读写/tmp目录中的文件
- 系统在启动时自动删除/tmp目录的所有文件。
7.1 创建本地临时文件
- mktemp会在本地目录中创建一个文件。
- 要用mktemp命令在本地目录中创建一 个临时文件,你只要指定一个文件名模板就行了。模板可以包含任意文本文件名,在文件名末尾 加上6个X就行了。
- mktemp命令会用6个字符码替换这6个X,从而保证文件名在目录中是唯一的。
1 | |
7.2 在/tmp 目录创建临时文件
- -t 选项会强制mktemp命令来在系统的临时目录来创建该文件。在用这个特性时,mktemp命 令会返回用来创建临时文件的全路径,而不是只有文件名。
1 | |
- 案例:
1 | |
7.3 创建临时目录
-d 选项告诉mktemp命令来创建一个临时目录而不是临时文件。
案例:
1 | |
8. 记录消息
- tee命令相当于管道的一个T型接头。它将从STDIN过来的数据同时发往两处。一处是 STDOUT,另一处是tee命令行所指定的文件名:
1 | |
- 默认情况下,tee命令会在每 次使用时覆盖输出文件内容。如果你想将数据追加到文件中,必须用-a选项。
参考文献

Linux shell(5)-呈现数据
https://oldstory.cn/2022/01/12/linux_shell_5_cheng_xian_shu_ju/